Metal Core PCB Manufacturer, We are 100um to 7200um Heavy copper PCBs and Extra thick copper PCBs Vendor, we offer the Metal core PCBs from 1 layer to 20 layers.
In the fast-paced world of modern electronics, Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) have emerged as the cornerstone of innovation. With a relentless pursuit of enhanced efficiency, reliability, and performance in electronic devices, Metal Core PCBs have become the preferred solution for manufacturers worldwide. Join us as we embark on a journey into the realm of Metal Core PCBs, uncovering their intricate design, diverse materials, sophisticated manufacturing processes, wide-ranging applications, unparalleled advantages, and addressing common queries along the way.
What is a Metal Core PCB?
Metal Core PCB is a specialized printed circuit board whose core feature is the use of a metal substrate, usually aluminum or copper, as the base instead of traditional fiberglass. This metal substrate has superior thermal conductivity, making metal substrate printed circuit boards very suitable for applications that require efficient heat dissipation.
Metal substrate printed circuit board is a composite structure composed of metal substrate, copper foil layer and insulation layer. Among them, the metal substrate serves as the main heat conduction channel, which can quickly transmit the heat generated by electronic components, effectively reduce the temperature of the equipment, and improve stability and reliability. In contrast, traditional glass fiber substrates have poor thermal conductivity and are difficult to meet the heat dissipation performance requirements of high-power and high-density electronic equipment.
In some specific application areas, metal substrate printed circuit boards have shown obvious advantages. For example, LED lighting, automotive electronics, communication equipment and other fields have high requirements for heat dissipation performance. At this time, using metal substrate printed circuit boards can effectively solve the problem of equipment failure caused by heat accumulation. In addition, metal substrate printed circuit boards are also widely used in high-power applications such as some industrial control equipment, power modules, and solar inverters.
In general, metal substrate printed circuit boards provide reliable guarantee for the stable operation of electronic equipment through superior thermal conductivity. As the requirements for power density and heat dissipation performance of electronic products continue to increase, metal substrate printed circuit boards will play an increasingly important role in various fields.
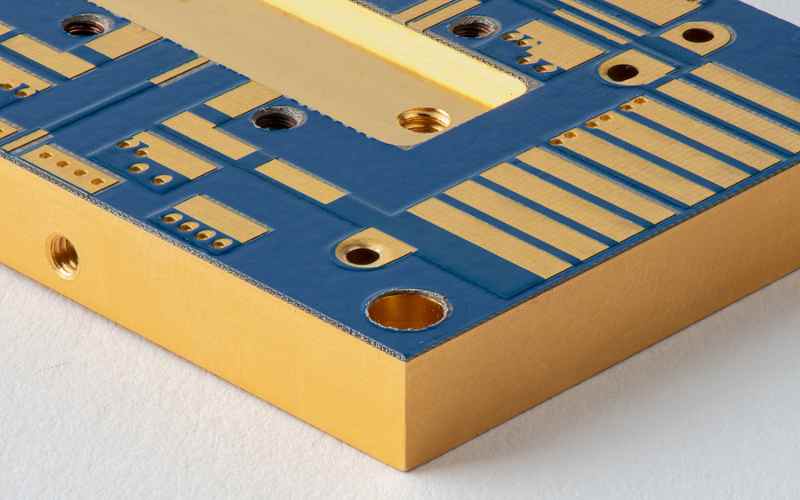
Metal Core PCB
Metal Core PCB design Reference Guide.
When designing metal substrate PCBs, engineers need to carefully consider factors such as thermal management, electrical connections, and mechanical stability. They must optimize the layout to ensure optimal heat transfer while maintaining signal integrity and reliability.
First, thermal management is one of the crucial considerations in metal substrate PCB design. Metal substrates have a higher thermal conductivity than traditional fiberglass substrates, allowing them to more efficiently disperse the heat generated by electronic components. During the design process, engineers need to rationally layout heat sinks or heat dissipation channels to ensure that heat can be quickly transferred from electronic components to the metal substrate and released to the surrounding environment through appropriate heat dissipation.
Secondly, electrical connections are an aspect that cannot be ignored in metal substrate PCB design. Engineers must ensure circuit connectivity and stability to ensure signals are transmitted accurately and unaffected by external interference. To do this, they need to accurately plan the path and spacing of wires to avoid signal crosstalk and electrical interference, and take appropriate shielding measures to ensure stable operation of the circuit.
Finally, mechanical stability is another key consideration in metal substrate PCB design. Metal substrates are more rigid and durable than traditional fiberglass substrates and can better resist the effects of mechanical stress and vibration. During the design process, engineers need to ensure that the connection between the electronic components and the metal substrate is strong and reliable to prevent breakage or loosening due to mechanical stress, thereby improving the reliability and life of the PCB.
In short, designing a metal substrate PCB requires comprehensive consideration of thermal management, electrical connections, and mechanical stability. Through reasonable layout and design, engineers can ensure that metal substrate PCBs have excellent thermal properties, stable electrical properties, and reliable mechanical properties to meet the needs of various application scenarios.
What material is used in Metal Core PCB?
Metal Core PCBs (Metal Substrate Printed Circuit Boards) come in a variety of materials, with aluminum and copper being the most common core material choices. The metal core provides excellent thermal conductivity and is suitable for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. Between the metal core and the copper foil layer, there is usually a layer of thermally conductive dielectric, which is usually a dielectric layer with good thermal conductivity.
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with good thermal conductivity, so it is often chosen as the core material when manufacturing Metal Core PCBs. Its thermal conductivity can effectively conduct heat generated by electronic components and maintain the stability of the circuit board. On the other hand, copper is widely used in the PCB industry due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It is often used as one of the core materials of Metal Core PCB to provide reliable electrical connections.
The dielectric layer between the metal core and the copper foil is usually a special thermally conductive medium. This medium provides both good electrical isolation and efficient heat conduction. This design ensures that Metal Core PCB can effectively dissipate heat in high-power applications while maintaining circuit reliability and stability.
In general, the material selection of Metal Core PCB takes full consideration of thermal management and electrical performance, ensuring that electronic devices can maintain stability when operating at high power and providing a reliable foundation for innovative applications.
What size are Metal Core PCB?
Metal-based PCBs come in a variety of sizes, ranging from small, complex designs for consumer electronics to large, high-power configurations for industrial applications. Its size depends on the specific requirements of the electronic device and its intended use.
For consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and smart wearable devices, metal-based PCBs typically come in smaller sizes. These devices require a compact design to be lightweight and portable, and need to have excellent heat dissipation performance to ensure stable operation over a long period of time.
For industrial applications, such as power modules, motor drivers, and high-power LED lighting systems, metal-based PCBs tend to have larger sizes. These devices need to handle higher power and current, so the PCB needs to have a larger heat dissipation surface area to effectively dissipate the heat and ensure the reliability and long-term stability of the device.
In addition, metal-based PCBs are also widely used in fields such as medical equipment, aerospace instruments, and military equipment. In these areas, PCB dimensions may vary depending on application requirements, ranging from tiny devices to large systems.
Therefore, metal-based PCBs are flexible in size and can meet the needs of different fields and applications. Manufacturers can customize PCBs in various sizes and shapes according to customers’ specific requirements to ensure optimal performance and suitability.
The Manufacturer Process of Metal Core PCB.
The manufacturing process of metal-based PCBs involves several key steps, including substrate preparation, copper patterning, dielectric layer lamination, solder film coating, and surface treatment. First of all, the substrate preparation stage is one of the important steps in manufacturing metal-based PCBs. At this stage, engineers select an appropriate metal-based material, usually aluminum or copper, and then surface-treat it to ensure good adhesion and flatness.
Next comes the copper patterning step, which is the process of forming electrical connections on the surface of a metal substrate. Using techniques such as photolithography and etching, engineers pattern the required circuit patterns on the copper foil layer to facilitate subsequent circuit connections.
This is followed by dielectric lamination, a step that involves laminating the thermally conductive dielectric layer to the copper foil layer and metal substrate. This dielectric layer has excellent thermal conductivity and can effectively conduct the heat generated by the electronic device into the metal substrate, thereby achieving effective heat dissipation.
Then comes the solder film coating stage, where engineers will apply a layer of solder film on the surface of the metal-based PCB to achieve reliable solder connections when assembling electronic components. The selection and coating process of welding film are crucial to ensure welding quality.
Finally, there is the surface treatment, a step designed to provide the metal-based PCB with the desired surface properties, such as corrosion protection, enhanced electrical conductivity, and improved soldering performance. Common surface treatment methods include gold plating, tin spraying, lead spraying, etc.
In addition to the above basic steps, manufacturing metal-based PCBs also requires the use of some advanced technologies to optimize performance, such as controlled impedance routing and thermal vias. These technologies can ensure that metal-based PCBs perform well in harsh environments such as high frequency and high power and meet the needs of various applications.
Through the application of these key steps and advanced technologies, metal-based PCB manufacturers can provide high-quality, high-performance products and provide solid support for the development and innovation of the electronics industry.
The Application area of Metal Core PCB.
Metal-based PCBs are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, LED lighting, power electronics, and telecommunications. Metal-based PCBs play an important role in LED street lights, automotive engine control modules, power converters, and high-power amplifiers.
In the automotive industry, metal-based PCBs are widely used in automotive engine control modules, in-car entertainment systems and body electronics. They can operate stably in high-temperature environments and have excellent heat dissipation properties, helping to improve the reliability and performance of automotive electronic systems.
In the aerospace field, metal-based PCBs are used in key components such as aircraft instruments, communication systems and navigation equipment. They are lightweight yet strong and can withstand extreme temperatures and vibrations, ensuring stable operation of avionics equipment.
In the field of LED lighting, metal-based PCBs are widely used in products such as LED street lights, indoor lighting, and stage lighting. They can effectively dissipate heat, extend the life of LED lights, and provide stable light output.
In the field of power electronics, metal-based PCBs are used in equipment such as power converters, inverters and chargers. They are able to withstand high power density and high current, providing stable and reliable power output.
In the telecommunications industry, metal-based PCBs are used in communication base stations, network equipment and satellite communication systems. They can provide excellent signal transmission performance and have anti-interference and anti-electromagnetic interference properties to ensure the stable operation of communication equipment.
In summary, metal-based PCBs play an important role in various industries, providing critical support for the high performance and reliability of modern electronic devices. With the continuous advancement of technology, the application fields of metal-based PCBs will be further expanded, promoting the continued development of the electronics industry.
What are the advantages of Metal Core PCB?
Metal Core PCBs have many advantages over traditional PCBs, including the following:
Excellent thermal management
The metal core plate provides efficient heat conduction, allowing electronic components to operate at lower temperatures, thereby increasing overall reliability. In high-power electronic devices, thermal management is critical. The thermal conductivity properties of metal core boards make them a preferred choice, effectively transferring heat away from electronic components and maintaining stable operation of the equipment.
Excellent mechanical stability
Metal core PCBs offer higher stiffness and durability than standard PCBs, making them suitable for harsh environments and high-vibration applications. In industries such as automobiles and aerospace, metal core PCBs can withstand large vibrations and impacts to ensure stable operation of equipment.
Higher power handling capabilities
Metal core PCBs are capable of handling higher current and power densities, making them ideal for high-power electronic devices. In fields such as high-power LED lighting and power converters, metal core PCBs can operate stably and reliably to ensure the performance of the equipment.
Compact design
Because metal core PCBs have superior thermal properties, they enable more compact designs and higher component density, saving valuable electronic component space. Today, as electronic components become more and more integrated, metal core PCBs can meet designers’ needs for miniaturization and lightweight, making equipment more compact and efficient.
These advantages of metal core PCB make it an indispensable electronic component in various industries, driving continuous innovation and progress of technology. In the future, as the demand for high performance and high reliability in electronic equipment continues to increase, metal core PCBs will continue to play an important role and provide strong support for the development of various industries.
FAQ
What is the manufacturing process of metal-based PCB?
The manufacturing process of metal-based PCB includes steps such as substrate preparation, copper patterning, dielectric layer lamination, pad coating and surface treatment. Compared with traditional PCBs, the key differences in the manufacturing process of metal-based PCBs are the selection of dielectric layers and the application of thermal management technology. In order to ensure excellent heat dissipation performance, metal-based PCBs usually achieve effective heat transfer through techniques such as drilling, milling, and pressurization.
How much does a metal-based PCB cost?
The cost of metal-based PCBs is usually slightly higher than traditional PCBs, mainly due to their special materials and manufacturing processes. However, in many applications, the superior performance and reliability of metal-based PCBs can often offset the additional cost and lead to longer-term performance and higher efficiency.
Are there any size restrictions for metal-based PCBs?
The size of metal-based PCBs is often limited by manufacturing equipment and processes, but in practice they can accommodate applications of all sizes. From small LED drivers to large industrial power modules, metal-based PCBs can meet different size and power needs.
 Professional Flip-Chip Packaging Substrate Supplier
Professional Flip-Chip Packaging Substrate Supplier
